By Alyssa Hill,
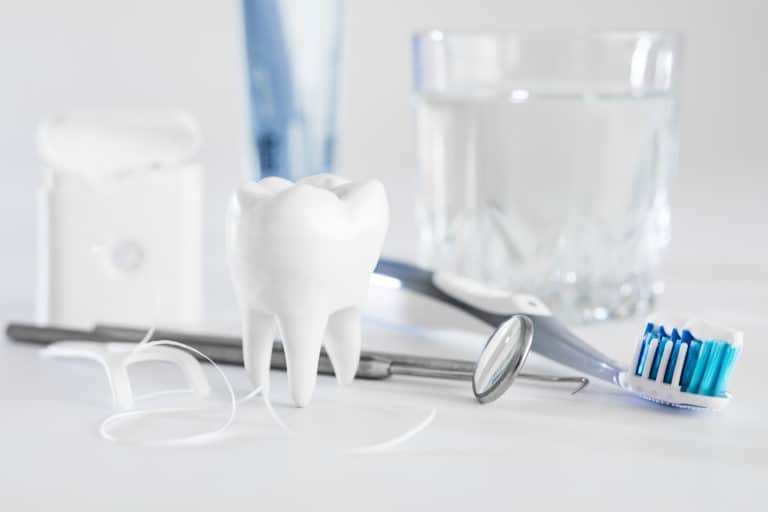
Drug addiction and abuse are global issues. Drug abuse refers to those who take illegal or legal substances, such as alcohol, excessively or in the wrong way. Addicts suffer from emotional, psychological, physical, behavioral, and nutritional issues. Damage to the liver, lungs, heart, and/or brain is also common. In addition, addicts are more likely to develop serious oral health conditions.
Abusers are typically able to quit and do not suffer from ‘codependency.’ Drug addiction, on the other hand, is when a person is physiologically and physically dependent on drugs.
Substances that can lead to poor oral health and general health outcomes include, but are not limited to:
- Tobacco — cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and cigars.
- Alcohol — beer, wine, and hard liquor.
- Natural Opiates — morphine, codeine, and thebaine.
- Synthetic Opiates — hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and heroin.
- Cannabis — inhaling cannabis through smoking or vaporization.
- Amphetamines — benzedrine, adderall, and dexedrine.
- Abuse of Prescription Medications — sleeping pills, prescription opioids, amphetamines, ADHD medications, and morphine-based pain relievers.
- Illegal Drugs — cocaine, ecstasy, molly, and other “party drugs.”
Oral Health Effects — Tobacco and Nicotine
Nicotine is an extremely addictive chemical found in cigarettes, cigars, e-cigarettes, and chewing tobacco. It is one of the leading causes of disease and death in the United States. According to the CDC (2017), about 34 million adults in the United States smoke cigarettes. Consequently, Over 16 million cigarette smokers suffer from smoking-related diseases. Each day, about 2000 American teens under 18 years of age try their first cigarette and 300 of them become regular cigarette smokers.
Smoking is linked to heart diseases, respiratory diseases, lung cancer, and serious oral health conditions, including:
Plaque and Calculus Buildup
Tobacco products contain chemicals that decrease saliva flow. As a result, if the mouth doesn’t produce enough saliva, plaque builds up faster and is harder to remove. Unremoved plaque turns into tartar (hardened plaque), which can only be removed professionally by a dentist. Over time, unremoved plaque and tartar results in cavities and gum disease.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Similar to plaque buildup, smokers are more likely to develop dry mouth. Xerostomia is a less serious oral condition that occurs when the mouth’s salivary glands do not produce enough saliva. Tobacco and nicotine slow down how quickly the mouth makes saliva, which can result in cavities, dental erosion, gum disease, mouth sores, and thrush, among others.
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Smoking cigarettes, chewing tobacco frequently, and using other tobacco products can lead to chronic bad breath.
Oral Cancer
Tobacco is the leading cause of oral cancer in adults. In fact, about 90 percent of people with oral cancer use tobacco. This type of cancer can affect the throat, tongue, mouth, lips, gums, or cheeks.
Gum Disease
Smoking on its own doesn’t result in gum disease. However, long-term smoking contributes to dry mouth, which leads to increased plaque and calculus buildup. Over time, gingivitis (reversible gum disease) or periodontal disease (PD) can form. PD results in permanent bone loss and eventually tooth loss.
Tooth Discoloration
Smoking can stain teeth brown, yellow, or black. Stains can be removed by a dentist, but smoking makes the discoloration more difficult to remove.
Changes in Blood Circulation
Smokers have “masked” or “silent” gum disease. This is because nicotine reduces blood flow, resulting in less sensitive gums and minor bleeding.
Oral Health Effects — Alcohol
Chronic alcoholism is an extremely progressive psychiatric illness that leads to uncontrollable alcohol consumption. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), moderate alcohol use is defined as one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men. Women who consume at least eight drinks a day and men who have at least 15 drinks per day are considered “heavy drinkers.” Excessive consumption of alcohol negatively impacts the teeth, oral cavity, and oral mucosa (mucous membrane lining inside the mouth).
Minor oral health conditions that may form due to long-term alcohol consumption include, but are not limited to:
- Similar to tobacco, tooth stains are a common side effect of long-term alcohol use. For example, if you prefer mixing drinks with dark sodas or drink red wine often, stains are more likely to develop. Sugary mixed drinks can also lead to cavities and erosion.
- Alcohol causes dehydration, which can result in dry mouth and chapped lips. To prevent these conditions, it is important to drink water while drinking alcohol to stay hydrated.
- Alcoholics are more likely to neglect oral care and have more plaque buildup than non-drinkers. Often times, they are preoccupied with drinking and usually forget to brush their teeth and visit a dentist for regular teeth cleanings.
- Drinking alcohol excessively doubles a person’s chance of developing bruxism (teeth grinding).
More serious oral health conditions that can develop from long-term alcohol abuse and addiction include:
Dental Erosion
Dental erosion occurs when acidic substances wear away tooth enamel. The condition is irreversible because enamel cannot regrow. Excessive, long-term alcohol consumption can induce dental erosion. Enamel erosion associated with alcoholism can be linked to frequent vomiting, regurgitation, or consuming alcoholic drinks high in acidity. For example, the pH levels in most wines are low, which may result in erosion over time.
Dental Caries & Periodontal Disease
Poor oral hygiene is a common trait in alcoholics. In addition, alcohol’s drying effect can contribute to the formation of plaque, a sticky bacterial layer that triggers an inflammatory response in the gums. As a result, if plaque isn’t removed completely, tartar (hardened plaque) and cavities will develop over time. If the tartar spreads below the gumline, periodontal disease commonly forms. If the disease is left untreated, permanent bone loss and possible tooth loss can occur.
Mouth Sores & Oral Cancer
Heavy drinking is the second leading cause of oral cancer in adults. People who have at least four drinks a day are about five times more likely to develop mouth or throat cancer compared to those who never drink or drink moderately.
Oral Health Effects — Drug Addiction & Abuse of Prescription Medications
Long-term addiction to certain drugs, such as natural opiates, synthetic opiates, amphetamines, and psychoactive drugs, can result in serious oral health complications. For example, cavities and gum diseases, such as periodontal disease, are more prevalent in addicts than in non-drug users. This is because addicts do not visit dentists regularly (twice a year) and therefore have more plaque buildup on their teeth. Some drugs also weaken the immune system (e.g. cocaine), which increases an addict’s risk of developing oral infections. Similar to tobacco and nicotine, drug addiction can also lead to:
- Plaque and tartar buildup, resulting in cavities.
- Dry mouth and bad breath.
- Tooth discoloration and hard-to-remove stains.
- Gum diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontal disease.
- Loss of blood flow to roots and gums (silent gum disease).
- Oral cancers (cancerous ulcers affecting the mouth, throat, and surrounding areas).
In addition, long-term drug addiction can cause:
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Bruxism, which is the habit of grinding teeth while sleeping or throughout the day, affects about 90 percent of the U.S. population. Some children outgrow the habit, while others do not. However, bruxism can also be induced by long-term drug abuse or addiction. Certain drugs that may cause teeth grinding include psychotropics (psychoactive drugs). These stimulant drugs are chemical substances that change how the brain functions, which results in drastic mood, behavioral, and cognitive changes. Commonly prescribed psychoactive drugs include Xanax, Zoloft, Celexa, Prozac, Ativan, Lexapro, and other antidepressants.
Nutritional Deficiencies, High Sugar Intake & Neglected Oral Care
Drug addicts are less likely to visit the dentist, doctor, or take care of themselves in general. This is because once they are dependent on a substance, they only care about getting more of that drug. As a result, addicts do not brush their teeth regularly and usually only eat inexpensive foods that are high in sugar. Depending on the drug, some people stop eating altogether, which results in malnutrition. All of these factors lead to poor dental health, including large cavities, gum diseases, dry mouth, and possible tooth loss, among others.
Commonly Abused Drugs and Medications
Many drugs have negative effects on an individual’s oral health. For example, some commonly used drugs that harm the oral cavity include:
Cocaine
Frequent cocaine users are more likely to develop oral infections because the drug has immunosuppressive effects, which weakens the immune system. Cocaine addicts have a higher chance of developing cavities, gum diseases, gingival lesions, nasal damage, bruxism, and temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD).
Ecstasy or Molly
Ecstasy is an amphetamine (a psychoactive drug) that alters bodily sensations and increases energy. It is an illegal substance that people take recreationally. Long-term use of ecstasy can lead to dry mouth, cavities, dental erosion, bruxism, and other mucosal changes.
Heroin
Heroin is a synthetic and highly addictive opioid drug that is processed from morphine (a natural opiate). Addiction to this drug is directly correlated with poor oral hygiene due to bad personal hygiene and long-term malnutrition. Periodontal disease, abnormally high levels of tooth decay, and dental trauma are also common in heroin addicts. Many addicts clench or grind their teeth and experience tenderness in the jaw muscles.
Methamphetamine (Meth)
Chronic addiction to methamphetamine can result in “meth mouth,” which is characterized by large cavities, fractured teeth, and poor dental health. Common signs of meth mouth include dry mouth, cracked teeth, lockjaw, periodontal diseases, cavities along the gum lines of the teeth, bruxism, rotting teeth, and bad breath. Meth addicts typically lose teeth, especially if they do not receive treatment.
Cannabis
Cannabis, also known as marijuana, is a common medical and recreational drug. Frequent cannabis users typically have poorer oral health standings than non-users. They are more likely to develop dental caries (cavities), periodontal diseases, oral lesions, and dry mouth. Heavy marijuana use also causes greenish-brown stains on the teeth.
Certain Prescription Medications (Long-Term Abuse)
Long-term addiction or abuse of prescription medication can lead to serious oral conditions, such as cavities, gum diseases, and dry mouth. Common drugs include Adderall (ADHD medication), sleeping pills, opioids, and prescription-based pain relievers (such as morphine).
Finding Help for Your Addiction
If you or a loved one are suffering from nicotine, alcohol, or drug addiction, it is crucial to seek treatment. In addition to finding an addiction treatment center and/or mental health facility, oral health treatment should also be a high priority. If you are experiencing any issues related to dental health, such as abnormal development of cavities, gum inflammation, sensitive teeth, or unexpected tooth loss, visit a general dentist or dental specialist as soon as possible to explore your treatment options.
Source: https://www.newmouth.com
Disclaimer: We at Prepare for Change (PFC) bring you information that is not offered by the mainstream news, and therefore may seem controversial. The opinions, views, statements, and/or information we present are not necessarily promoted, endorsed, espoused, or agreed to by Prepare for Change, its leadership Council, members, those who work with PFC, or those who read its content. However, they are hopefully provocative. Please use discernment! Use logical thinking, your own intuition and your own connection with Source, Spirit and Natural Laws to help you determine what is true and what is not. By sharing information and seeding dialogue, it is our goal to raise consciousness and awareness of higher truths to free us from enslavement of the matrix in this material realm.
 EN
EN FR
FR























It is nice article.It is useful and helpful post.dental implants Columbus.Thank you for sharing this post.